移动零
给定一个数组 nums,编写一个函数将所有 0 移动到数组的末尾,同时保持非零元素的相对顺序。
请注意 ,必须在不复制数组的情况下原地对数组进行操作。
双指针问题。
慢指针指向非零元素应当被放置的地方,快指针负责遍历整个数组寻找非零元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| class Solution {
public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
int slow = 0;
int fast = 0;
while (fast < nums.length)
{
if (nums[fast] != 0)
{
int temp = nums[slow];
nums[slow] = nums[fast];
nums[fast] = temp;
slow++;
}
fast++;
}
}
}
|
优化,减少操作次数,只有slow和fast不重合才交换
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| class Solution {
public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
int slow = 0;
int fast = 0;
while (fast < nums.length)
{
if(nums[fast] != 0 )
{
if(fast != slow) {
int temp = nums[fast];
nums[fast] = nums[slow];
nums[slow] = temp;
}
slow++;
}
fast++;
}
}
}
|
注意索引要小于数组长度不能去等
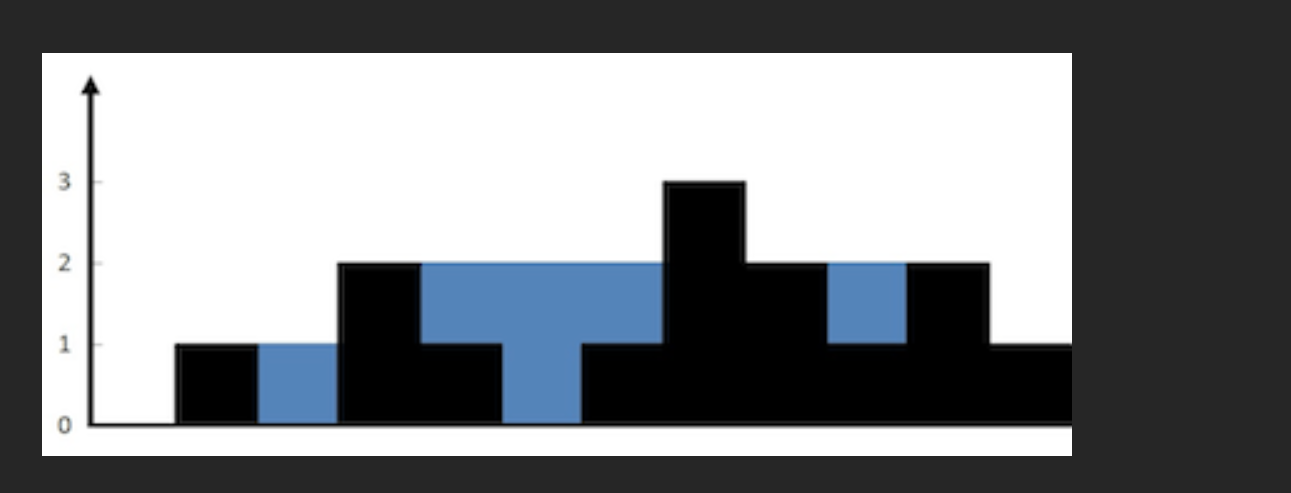
盛水容器
给定一个长度为 n 的整数数组 height 。有 n 条垂线,第 i 条线的两个端点是 (i, 0) 和 (i, height[i]) 。
找出其中的两条线,使得它们与 x 轴共同构成的容器可以容纳最多的水。
返回容器可以储存的最大水量。
说明:你不能倾斜容器。
![img.png image]()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| class Solution {
public int maxArea(int[] height) {
int i = 0;
int j = height.length - 1;
int result = (j - i) * Math.min(height[i],height[j]);
while (i < j)
{
int resultThisLoop;
if(height[i] <= height[j])
{
i++;
}else{
j--;
}
resultThisLoop = (j - i) * Math.min(height[i],height[j]);
result = Math.max(result,resultThisLoop);
}
return result;
}
}
|
风格可以优化一下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| class Solution {
public int maxArea(int[] height) {
int i = 0;
int j = height.length - 1;
int result = 0;
while (i < j) {
int area = (j - i) * Math.min(height[i], height[j]);
result = Math.max(result, area);
if (height[i] <= height[j]) {
i++;
} else {
j--;
}
}
return result;
}
}
|
三数之和
给你一个整数数组 nums ,判断是否存在三元组 [nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]] 满足 i != j、i != k 且 j != k ,同时还满足 nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] == 0 。请你返回所有和为 0 且不重复的三元组。
注意:答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
去掉一个元素后,变成了一个给定0-nums[i]的关于其他元素两数之和。考虑用哈希集合先去重,其他两数之和的子数组规定为选取的i索引之后的元素。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int target = 0 - nums[i];
List<Integer> resultThisLoop = twoSum(target,i,nums);
resultThisLoop.add(nums[i]);
}
}
}
|
卡壳了,本来想套用标准两数之和的问题但无法解决。但是标准两数之和只能获得一个解,不保证获得全部
因此如下思路:
- 特殊情况判断:length小于3直接返回空列表
- 排序:升序排序,为了方便使用双指针法从两端向中间移动,同时便于跳过重复元素,避免产生重复的三元组
- 遍历和双指针:
- 遍历,
- 去重,如果nums[i] 和nums[i-1]相同跳过当前循环
- 剪枝:如果nums[i]大于0,因为数组以及有序门之后的数都比他大,直接结束整个循环
- 双指针:在for的内部,定义两个指针left和right。
- 问题转化成在i+1到legnth-1找两个数,使总和为0
- 在left<right的前提进行循环:
- sum == 0则得到解,添加结果,之后left右移到第一个不同的元素处(去重),right左移到第一个不同的元素处
- sum < 0:太小了,要增大,left右移一位(right不能右移一位,因为right最开始是在最右侧,是从右侧向左移动的,如果移动回去会导致重复)
- sum > 0:太大了,要减小,right左移一位
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
| import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
int length = nums.length;
if (length < 3) {
return null;
}
Arrays.sort(nums);
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if (i>0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1])
{
continue;
}
if (nums[i] > 0)
{
break;
}
int left = i + 1;
int right = length - 1;
while (left < right) {
int sum = nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right];
if(sum == 0)
{
result.add(new ArrayList<>(List.of(nums[i],nums[left],nums[right])));
while (left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 1])
{
left++;
}
while (left < right && nums[right] == nums[right - 1])
{
right--;
}
left++;
right--;
}
else if (sum < 0)
{
left++;
}
else if (sum > 0)
{
right--;
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
|
时间复杂度:O(n^2),空间O(logn)(排序需要logn)
下面是力扣官方题解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
Arrays.sort(nums);
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
for (int first = 0; first < n; ++first) {
if (first > 0 && nums[first] == nums[first - 1]) {
continue;
}
int third = n - 1;
int target = -nums[first];
for (int second = first + 1; second < n; ++second) {
if (second > first + 1 && nums[second] == nums[second - 1]) {
continue;
}
while (second < third && nums[second] + nums[third] > target) {
--third;
}
if (second == third) {
break;
}
if (nums[second] + nums[third] == target) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(nums[first]);
list.add(nums[second]);
list.add(nums[third]);
ans.add(list);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}
|
复杂度一样。
因为second是在向右移动,b在增加,所以c一定要减小,third只能单调向左移动
接雨水
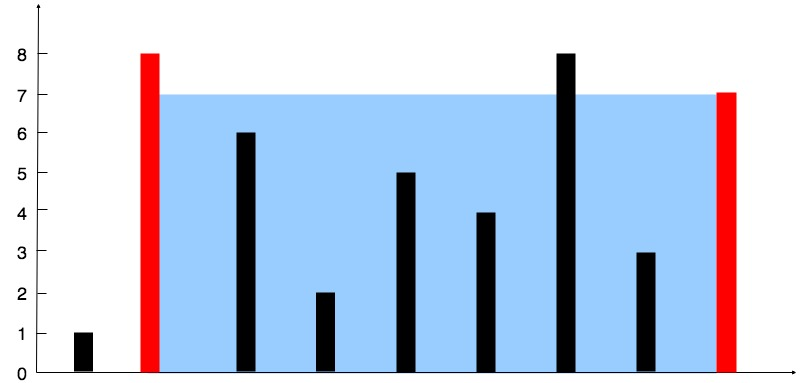
给定 n 个非负整数表示每个宽度为 1 的柱子的高度图,计算按此排列的柱子,下雨之后能接多少雨水。
![img_1.png image]()
输入:height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]
输出:6
解释:上面是由数组 [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] 表示的高度图,在这种情况下,可以接 6 个单位的雨水(蓝色部分表示雨水)。
一开始的思考:卡壳错误,但这种想法类似单调栈法
0. length小于3则直接返回0
- left,right(从left+1开始) 指针进行遍历。
- 每个left,看right是否小于left
- 小于,依次遍历right+1,+2……直到
- 遇到大于left高度的,记录宽度和left算体积,left更新为right,right更新为left+1
- 到了边上,则更新left为left+1,right为left+1继续遍历
- 大于,left++,right++
- 直到left = length - 2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
if (height.length < 3)
{
return 0;
}
int left = 0;
int right = left + 1;
int result = 0;
while (left < height.length - 2 && left < right)
{
if (height[left] <= height[right])
{
left++;
right = right + 1;
}else{
while (left < right && left < height.length - 2) {
int volum_of_bolum = height[right];
right++;
boolean heigherThanOrEqual_to_Left = false;
while (right < height.length) {
if (height[right] >= height[left]) {
heigherThanOrEqual_to_Left = true;
result += height[left] * (right - left - 1) - volum_of_bolum;
left = right;
right = left + 1;
break;
}
volum_of_bolum += height[right];
right++;
}
if (heigherThanOrEqual_to_Left == false) {
left++;
right = left + 1;
}
left++;
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
|
以上逻辑非常麻烦,不好。但是和单调栈法有相同的地方,见最后
下面是正确的分析
- 每个位置i,能接到的雨水高度取决于左右两边最高的柱子中较矮的哪个,之后再减去height[i]即可。即min(maxHeight_left,maxRight_right) - height[i]。对于每个i,可以分别遍历左侧和右侧得到结果。暴力算法时复杂度O(N^2)
- 进一步分解为两个对称的子问题,maxHeight_left和right。
- 对于maxHeight_left,发现每个遍历都有重复的遍历,有重叠子问题;并且maxHeight_left[i] = maX(maxHeight_left[i - 1],height[i]),满足最优子结构和无后效性。可以考虑动态规划
- 因此目标转化为用动态规划求解每个位置的maxHeight_left[i],
- 定义状态:i
- dp表:显然一维数组就够了(注意到可以滚动优化)
- 状态转移方程:dp_left[i] = maX(dp_left[i - 1],height[i]),子问题dp_left[i]就是求解索引为i的最大左侧高度。
- 确定边界条件:dp[0] = height[0]
- 确定状态转移顺序:每个dp都由左侧的dp[i-1]决定,因此从左向右遍历即可
- 之后类似分析maxHeight_right,转移方程dp[i] = max(dp[i + 1],height[i])
- 代入公式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
int result = 0;
int[] dp_left = new int[height.length];
int[] dp_right = new int[height.length];
dp_right[height.length-1] = height[height.length - 1];
dp_left[0] = height[0];
for (int i = 1; i < height.length; i++) {
dp_left[i] = Math.max(dp_left[i-1],height[i]);
dp_right[height.length - 1 -i] = Math.max(dp_right[height.length - i],height[height.length - 1 - i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < height.length; i++) {
result += Math.min(dp_left[i],dp_right[i]) - height[i];
}
return result;
}
}
|
这个实现时间复杂度是O(n),空间复杂度是O(n).
接下来可以尝试进行空间优化。
每个高墙的计算,只依赖上一个状态和索引的值;水的计算,依赖于两侧高墙即可,可以双指针法
- left,从左侧开始遍历的指针
- right,从右侧开始遍历的指针
- left_max,从左侧开始left位置的最高墙
- right_max,从右侧开始到right的最高墙
- 但是每一刻怎么处理呢,我们并不知道某个索引位置的准确的左侧高墙和右侧高墙
可以分类
- left_max < right_max : 处理left索引即可。因为右侧高墙必定>=right_max>left_max
- left_max >= right_max : 处理rihgt索引即可。因为左侧高墙必当>=left_max>right>max
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| class Solution{
public int trap(int[] height){
int left = 0;
int right = height.length - 1;
int left_max = height[0];
int right_max = height[height.length - 1];
int result = 0;
while (left < right){
left_max = Math.max(height[left], left_max);
right_max = Math.max(height[right],right_max);
if (left_max < right_max){
result += left_max - height[left];
left++;
}else {
result += right_max - height[right];
right--;
}
}
return result;
}
}
|
下面是单调栈法:
- 单调栈:一个从栈底到栈顶大小是单调变化的栈,如果入栈的某个元素将要破坏单调性需要出栈直到满足单调性
- 这道题可以用单调栈找凹槽。我们把每个柱子的索引入栈,如果值是单调递减的,那么我们正在进入一个凹槽,如果将要入栈的元素i大于栈顶,则i是右墙,此时栈顶是槽底,出栈后的栈顶是左墙。由这三个元素可以确定大凹槽(如果存在的话)的在[槽底高度,左墙右墙最小值围城的高度]
- 其实相等于是一行一行计算水(在上面的解法都是竖着一列一列计算水)。如果有一个大凹槽,第一个弹出的栈底就是“绝对槽底”,这个槽底作为槽底高度,和弹出后的栈底以及当前元素可以 算出一个水量,之后相当于把这些填起来。在然后比较当前元素和新栈底是否是单调递减,不是的话继续,把新栈顶作为新的槽底高度,新栈顶弹出后下一个栈顶以及当前元素作为左右墙。以此类推
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| import java.util.Deque;
class Solution {
public int trap(int height[]) {
int result = 0;
Deque<Integer> stack = new ArrayDeque();
for (int i = 0; i < height.length; i++) {
while (!stack.isEmpty() && height[i] > height[stack.peek()])
{
int mid = stack.pop();
if (stack.isEmpty())
{
break;
}
int left = stack.peek();
int h = Math.min(height[left],height[i]) - height[mid];
int w = i - left - 1;
result += h * w;
}
stack.push(i);
}
return result;
}
}
|
Deque的接口方法:
| 操作类型 |
在头部操作 (First Element) |
在尾部操作 (Last Element) |
| 插入 (Insert) |
addFirst(e): 失败时抛出异常 |
addLast(e): 失败时抛出异常 |
|
offerFirst(e): 失败时返回 false |
offerLast(e): 失败时返回 false |
| 移除 (Remove) |
removeFirst(): 队列为空时抛出异常 |
removeLast(): 队列为空时抛出异常 |
|
pollFirst(): 队列为空时返回 null |
pollLast(): 队列为空时返回 null |
| 检查 (Examine) |
getFirst(): 队列为空时抛出异常 |
getLast(): 队列为空时抛出异常 |
|
peekFirst(): 队列为空时返回 null |
peekLast(): 队列为空时返回 null |
| 栈操作 (Stack Operation) |
等效的 Deque 方法 |
描述 |
| 入栈 (Push) |
push(e) |
在队列头部添加一个元素。它完全等同于 addFirst(e)。 |
| 出栈 (Pop) |
pop() |
移除并返回队列头部的元素。它完全等同于 removeFirst()。如果队列为空,会抛出异常。 |
| 查看栈顶 (Peek) |
peek() |
返回队列头部的元素,但不移除。它完全等同于 peekFirst()。如果队列为空,返回 null。 |
| 队列操作 (Queue Operation) |
等效的 Deque 方法 |
描述 |
| 入队 (Add/Offer) |
add(e) / offer(e) |
在队列尾部添加一个元素。add(e) 等同于 addLast(e),offer(e) 等同于 offerLast(e)。 |
| 出队 (Remove/Poll) |
remove() / poll() |
移除并返回队列头部的元素。remove() 等同于 removeFirst(),poll() 等同于 pollFirst()。 |
| 检查队头 (Element/Peek) |
element() / peek() |
返回队列头部的元素,但不移除。element() 等同于 getFirst(),peek() 等同于 peekFirst()。 |
deque的栈顶是队头,在作为栈和队列时逻辑是不同的。因此对于一个deque,要么是栈要么是队列不要混用